In addition to 4K TVs and smart TVs, the most popular TV sets are OLED TVs. OLED TV is also known as OLED organic television. Its body can be as thin as paper, can be matched with different decoration styles, and even be integrated into one. Moreover, the more astounding the picture performance of OLED TVs is, the picture quality is not only clear and natural, but also the playback is very smooth. Having said so much, what is OLED TV? What is the process and what screen is used, and what is the difference between it and an ordinary LED TV?

What is OLED TV?
OLED means "organic light-emitting diodes" and is the latest display screen technology. "OLED TV" was first proposed by LG. OLED TV adopts the latest display technology, and LCD LCD panels are no longer needed. RGB color signals are directly displayed by OLED diodes, and there is almost no problem with the viewing angle of LCD.
The basic structure of an OLED is composed of a thin and transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) with a semi-conductor characteristic, which is connected to the positive electrode of electricity, and another metal cathode, which is formed into a sandwich structure. The entire structural layer includes a hole transport layer (HTL), a light emitting layer (EL) and an electron transport layer (ETL). When the power is supplied to an appropriate voltage, positive hole and cathode charges are combined in the light emitting layer to produce light, and red, green, and blue RGB primary colors are generated according to different recipes to form a basic color.
Second, OLED TV technology
1, Samsung OLED technology
What is Samsung OLED RGB technology? In fact, this RGB (tricolor) independent pixel glow full color technology. Each pixel has three red, green and blue light emitting components, namely three OLED light emitting diodes. In other words, the implementation of pixel color requires three kinds of OLED light emitting materials. The advantages of OLED RGB technology are good color display and high contrast. The disadvantages are also obvious, that is, the required pixel material is more and the cost is high. And need to control more pixels, more difficult in color control.
2, LG OLED technology
What is the combination of OLED white light and filter, which is dominated by LG Display? The pixel of this technology is actually a white light emitting diode, and the white light emitting OLED diode is covered with red, blue, and green primary light filters. The number of OLED diodes required is small and only three filter films are required. Its advantages are very prominent, namely low production technology and cost. However, the disadvantage is that the use of a filter film results in contrast, brightness, and color performance without the advantages of OLED RGB technology.
3, Panasonic OLED TV technology
1) New OLED printing technology
Panasonic's official explanation for the solution of high-precision, large-size OLED panels is the adoption of new printing technologies. The printing technology is widely used in the LCD era. The simple understanding is to determine the dot pitches of three RGB sub-pixels. Can be produced. It has the advantages of lower cost and lower manufacturing process requirements.
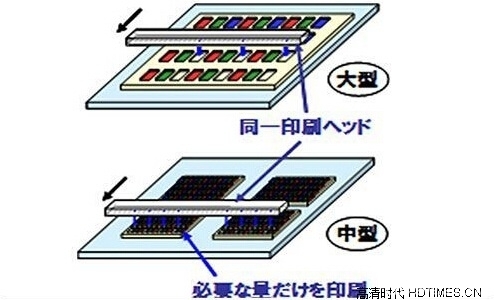
Since the OLED has various processes such as FMM (Fine Metal Mask) and white OLED+CF (White OLED plus color filter), the manufacturing process of the FMM (Fine Metal Mask) needs to be manufactured by using the vapor deposition method. As the yield rate is lower, it is also necessary to cut the glass substrate before the large-size panel is manufactured. The 55-inch OLED TV exhibited by Samsung is manufactured based on this process.
The white light OLED+CF mode uses a similar liquid crystal to place the white OLED on the bottom, and then the light passes through the color filter, which is slightly inferior in terms of power consumption and color.
In this way, a printed OLED can be basically painted directly on a large-sized glass. Compared with the above two, it does not require a high-temperature vacuum environment and can achieve better performance. It should be regarded as an ideal technology. However, printing OLEDs also has its own shortcomings. One of the difficulties in the OLED production process is that organic materials need to be maintained in a vacuum-stabilized environment, otherwise their lifetime will be affected.
The printing technology is difficult to ensure the life and luminous efficiency of blue paint. Although the Panasonic TV does not appear to have blue display problems, the overall picture has a slight yellowing phenomenon.
2) Top emission technology
In the display technology, Panasonic also used the “top emission†technology. A simple understanding is that OLEDs (organic light-emitting diodes) need to be energized between the cathode and the anode to emit light, while the cathode uses a transparent material. No light shielding of the panel improves the luminous efficiency.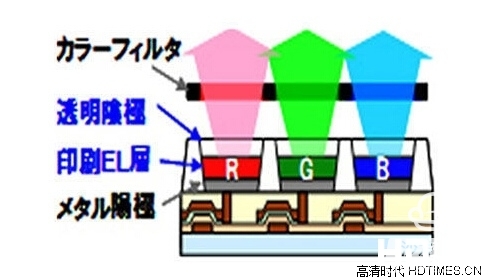
4, Sony OLED TV technology
1) Hybrid OLED panel
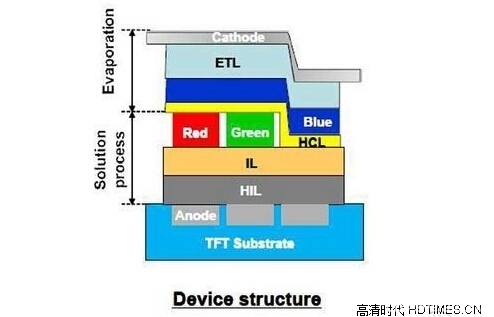
Although no detailed parameters of the panel were announced, Sony OLED uses a combination of vacuum evaporation and printing. Simply put, the specially developed technology for the OLED's lack of blue coating material and luminous efficiency as described above, the blue paint is first applied to form a common layer, and R, G red and green colors are printed first. Finally, the two are connected by evaporation, so that the life and luminous efficiency of the blue material are guaranteed. The obvious advantage is that Sony's live viewing of this OLED TV is perfect in both yellow and white and there is no problem of color cast.
Third, OLED TV display
1, OLED TV display has bright prospects, but the cost is high and it is difficult
Different from OLED and liquid crystal, the biggest difference is that there is no backlight system. It is a self-luminous material, like the plasma in the past, but it is lighter than a plasma screen. Therefore, the application prospect is very bright, but the light is bright and OLED is developed. The cost and difficulty of the screen are high.
Sony and Panasonic's OLED alliance have collapsed. It's not because the two companies are not optimistic about OLED technology. It's actually a downturn in their own business, so they don't have the energy to focus on OLED technology, such as Sharp, and they can only focus on energy. Continue to be in the field of liquid crystals.
2. Too few R&D members for OLED TV panels
Due to the withdrawal of Japanese companies, the OLED camp became thin, and now only the Korean-based LG and Samsung are still actively researching and developing. Of course, the mainland's panel companies have also made efforts. Companies such as China Star Optoelectronics and BOE are OLEDs. Supporters of technology, but the technical strength of the mainland is still relatively weak, and the core OLED panels can only be purchased from Korean manufacturers.
The two companies in the Korean industry are naturally overwhelmed, so the large-screen OLEDs have not received any news until recently. It was only once put on the agenda. Mainland manufacturers purchased OLED panels and expressed their desire to be third. Around the quarter introduced large-screen OLED devices.
3, OLED TV display life is relatively short, low yield
The lifetime problems of OLED panels will plague major technology manufacturers. The biggest problem with OLEDs so far is the short lifetime of blue OLED materials. In order to repair the defects of the blue OLED, a little more blue OLED material can be vapor-deposited, but the result is the color distortion phenomenon in the RGB structure. This is the fundamental reason why the color of the OLED screen is inconsistent. This blue substance is The small screen can still have a life of 10,000 hours, but large-sized devices, such as televisions, have a high requirement for longevity, so that the situation cannot be reconciled.
Fourth, OLED TV and LED TV difference
The difference between LED TV and OLED TV is mainly reflected in the screen display. How big is the difference between the HD movie playback? OLED technology is reliable, should wait for OLED or buy LCD.
Now LED TVs are border-lit LCDs (liquid crystal displays) that transmit light from a separate wire to the center of the screen through a large number of LEDs distributed around the screen. It thins the screen, but it also brings annoying viewing angle problems.
In contrast, the screen of an OLED (organic light emitting display) is composed of an organic material capable of emitting light when current passes through. Due to the elimination of the backlight, the performance of the OLED screen is superior to other competing products.
Fifth, OLED TV advantages
1, the thickness can be less than 1mm, only 1/3 of the LCD screen, and the weight is also lighter;
2, solid structure, there is no liquid material, so the shock resistance is good;
3, active light, width angle> 170 degrees, contrast> 10000: 1
4, the response time 5, low temperature characteristics, at minus 40 degrees can still display normally;
6, wide color gamut;
7, high luminous efficiency, energy consumption 8, can be manufactured on different substrates, can be made flexible display and light source;
VI. Shortcomings of OLED TV
1, life is usually only 5,000 hours, lower than the LCD at least 10,000 hours of life;
2. Mass production of large-size screens cannot be achieved, so it is currently only applicable to portable digital products;
3. There is a problem of insufficient color purity and it is not easy to show bright and rich colors.
Seventh, OLED TV development prospect
The problem of OLED TVs is very complicated. The R&D camp is too thin and technical breakthroughs have been delayed. As a result, the product yield rate is very low. This results in high costs, high panel prices, and high prices of natural terminal products. For example, the current OLED TV is priced at 29,999 yuan, but the LCD TV with the same size is priced at only 5,000 yuan, so the price difference, so that OLED TVs can only be high Shuaifu plaything.

What is OLED TV?
OLED means "organic light-emitting diodes" and is the latest display screen technology. "OLED TV" was first proposed by LG. OLED TV adopts the latest display technology, and LCD LCD panels are no longer needed. RGB color signals are directly displayed by OLED diodes, and there is almost no problem with the viewing angle of LCD.
The basic structure of an OLED is composed of a thin and transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) with a semi-conductor characteristic, which is connected to the positive electrode of electricity, and another metal cathode, which is formed into a sandwich structure. The entire structural layer includes a hole transport layer (HTL), a light emitting layer (EL) and an electron transport layer (ETL). When the power is supplied to an appropriate voltage, positive hole and cathode charges are combined in the light emitting layer to produce light, and red, green, and blue RGB primary colors are generated according to different recipes to form a basic color.
Second, OLED TV technology
1, Samsung OLED technology
What is Samsung OLED RGB technology? In fact, this RGB (tricolor) independent pixel glow full color technology. Each pixel has three red, green and blue light emitting components, namely three OLED light emitting diodes. In other words, the implementation of pixel color requires three kinds of OLED light emitting materials. The advantages of OLED RGB technology are good color display and high contrast. The disadvantages are also obvious, that is, the required pixel material is more and the cost is high. And need to control more pixels, more difficult in color control.
2, LG OLED technology
What is the combination of OLED white light and filter, which is dominated by LG Display? The pixel of this technology is actually a white light emitting diode, and the white light emitting OLED diode is covered with red, blue, and green primary light filters. The number of OLED diodes required is small and only three filter films are required. Its advantages are very prominent, namely low production technology and cost. However, the disadvantage is that the use of a filter film results in contrast, brightness, and color performance without the advantages of OLED RGB technology.
3, Panasonic OLED TV technology
1) New OLED printing technology
Panasonic's official explanation for the solution of high-precision, large-size OLED panels is the adoption of new printing technologies. The printing technology is widely used in the LCD era. The simple understanding is to determine the dot pitches of three RGB sub-pixels. Can be produced. It has the advantages of lower cost and lower manufacturing process requirements.

Since the OLED has various processes such as FMM (Fine Metal Mask) and white OLED+CF (White OLED plus color filter), the manufacturing process of the FMM (Fine Metal Mask) needs to be manufactured by using the vapor deposition method. As the yield rate is lower, it is also necessary to cut the glass substrate before the large-size panel is manufactured. The 55-inch OLED TV exhibited by Samsung is manufactured based on this process.
The white light OLED+CF mode uses a similar liquid crystal to place the white OLED on the bottom, and then the light passes through the color filter, which is slightly inferior in terms of power consumption and color.
In this way, a printed OLED can be basically painted directly on a large-sized glass. Compared with the above two, it does not require a high-temperature vacuum environment and can achieve better performance. It should be regarded as an ideal technology. However, printing OLEDs also has its own shortcomings. One of the difficulties in the OLED production process is that organic materials need to be maintained in a vacuum-stabilized environment, otherwise their lifetime will be affected.
The printing technology is difficult to ensure the life and luminous efficiency of blue paint. Although the Panasonic TV does not appear to have blue display problems, the overall picture has a slight yellowing phenomenon.
2) Top emission technology
In the display technology, Panasonic also used the “top emission†technology. A simple understanding is that OLEDs (organic light-emitting diodes) need to be energized between the cathode and the anode to emit light, while the cathode uses a transparent material. No light shielding of the panel improves the luminous efficiency.

4, Sony OLED TV technology
1) Hybrid OLED panel
Although no detailed parameters of the panel were announced, Sony OLED uses a combination of vacuum evaporation and printing. Simply put, the specially developed technology for the OLED's lack of blue coating material and luminous efficiency as described above, the blue paint is first applied to form a common layer, and R, G red and green colors are printed first. Finally, the two are connected by evaporation, so that the life and luminous efficiency of the blue material are guaranteed. The obvious advantage is that Sony's live viewing of this OLED TV is perfect in both yellow and white and there is no problem of color cast.

Third, OLED TV display
1, OLED TV display has bright prospects, but the cost is high and it is difficult
Different from OLED and liquid crystal, the biggest difference is that there is no backlight system. It is a self-luminous material, like the plasma in the past, but it is lighter than a plasma screen. Therefore, the application prospect is very bright, but the light is bright and OLED is developed. The cost and difficulty of the screen are high.
Sony and Panasonic's OLED alliance have collapsed. It's not because the two companies are not optimistic about OLED technology. It's actually a downturn in their own business, so they don't have the energy to focus on OLED technology, such as Sharp, and they can only focus on energy. Continue to be in the field of liquid crystals.
2. Too few R&D members for OLED TV panels
Due to the withdrawal of Japanese companies, the OLED camp became thin, and now only the Korean-based LG and Samsung are still actively researching and developing. Of course, the mainland's panel companies have also made efforts. Companies such as China Star Optoelectronics and BOE are OLEDs. Supporters of technology, but the technical strength of the mainland is still relatively weak, and the core OLED panels can only be purchased from Korean manufacturers.
The two companies in the Korean industry are naturally overwhelmed, so the large-screen OLEDs have not received any news until recently. It was only once put on the agenda. Mainland manufacturers purchased OLED panels and expressed their desire to be third. Around the quarter introduced large-screen OLED devices.
3, OLED TV display life is relatively short, low yield
The lifetime problems of OLED panels will plague major technology manufacturers. The biggest problem with OLEDs so far is the short lifetime of blue OLED materials. In order to repair the defects of the blue OLED, a little more blue OLED material can be vapor-deposited, but the result is the color distortion phenomenon in the RGB structure. This is the fundamental reason why the color of the OLED screen is inconsistent. This blue substance is The small screen can still have a life of 10,000 hours, but large-sized devices, such as televisions, have a high requirement for longevity, so that the situation cannot be reconciled.
Fourth, OLED TV and LED TV difference
The difference between LED TV and OLED TV is mainly reflected in the screen display. How big is the difference between the HD movie playback? OLED technology is reliable, should wait for OLED or buy LCD.
Now LED TVs are border-lit LCDs (liquid crystal displays) that transmit light from a separate wire to the center of the screen through a large number of LEDs distributed around the screen. It thins the screen, but it also brings annoying viewing angle problems.
In contrast, the screen of an OLED (organic light emitting display) is composed of an organic material capable of emitting light when current passes through. Due to the elimination of the backlight, the performance of the OLED screen is superior to other competing products.
Fifth, OLED TV advantages
1, the thickness can be less than 1mm, only 1/3 of the LCD screen, and the weight is also lighter;
2, solid structure, there is no liquid material, so the shock resistance is good;
3, active light, width angle> 170 degrees, contrast> 10000: 1
4, the response time 5, low temperature characteristics, at minus 40 degrees can still display normally;
6, wide color gamut;
7, high luminous efficiency, energy consumption 8, can be manufactured on different substrates, can be made flexible display and light source;
VI. Shortcomings of OLED TV
1, life is usually only 5,000 hours, lower than the LCD at least 10,000 hours of life;
2. Mass production of large-size screens cannot be achieved, so it is currently only applicable to portable digital products;
3. There is a problem of insufficient color purity and it is not easy to show bright and rich colors.
Seventh, OLED TV development prospect
The problem of OLED TVs is very complicated. The R&D camp is too thin and technical breakthroughs have been delayed. As a result, the product yield rate is very low. This results in high costs, high panel prices, and high prices of natural terminal products. For example, the current OLED TV is priced at 29,999 yuan, but the LCD TV with the same size is priced at only 5,000 yuan, so the price difference, so that OLED TVs can only be high Shuaifu plaything.