Home theater network () has a question for many audio enthusiasts, ordinary consumers and even some enthusiasts: there are many kinds of common audio formats, and they can pick no eye at all. Exaggeration, what is the difference between these different names? For volume portability, we should choose those formats. We should choose those formats for better sound. If we want to coexist, we should choose those formats?

As an audio device enthusiast, I also think that it is a music enthusiast, and the collection of albums and music files is not too small. For different audio formats, it can be said that the mainstream audio formats have not been used. The research has not been well understood for the technical aspects of its depth, but the difference between them can be simply shared.
And with the rise of DSD audio streams in the HiFi circle in recent years, in recent years, it has no longer been the PCM code monopoly audio file industry, DSD code stream has become a very mainstream format, and in this article, the author also Will briefly introduce the DSD audio file format and some personal views on the DSD audio format, friends may also leave their views on the DSD and PCM formats in the message area.
First of all, what is the PCM encoding format?
PCM Chinese called Pulse Code Modulation, which was developed in the late 1970s. CD, one of the recording media, was jointly launched by Philips and Sony in the early 1980s. The pulse code modulated audio format is also used by the DVD-A, which supports stereo and 5.1 surround sound, which was released and released in 1999 by the DVD Symposium. The bit rate of pulse code modulation is developed from 14-bit to 16-bit, 18-bit, 20-bit up to 24-bit; the sampling frequency is developed from 44.1 kHz to 192 kHz. The aspect of PCM pulse code modulation that can be improved and improved is getting smaller and smaller. Simply increasing the PCM pulse code modulation bit rate and sampling rate does not fundamentally improve its fundamental problem. The reason is that the main problems of PCM are:
(1) Any pulse code modulated digital audio system requires a sharply rising and falling filter at its input, allowing only the frequency of 20 Hz - 22.05 kHz to pass (the high end 22.05 kHz is determined by half the frequency of CD 44.1 kHz).
(2) Multi-stage or series-selected digital filters (reduced sampling frequency) during recording, multi-stage interpolated digital filters (increased sampling frequency) during playback, in order to control small signals during encoding The distortion, both of which require the addition of repeated quantitative noise. This limits the fidelity of PCM technology in audio reproduction.
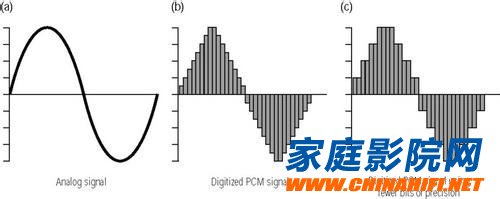
â–²The higher the bit rate, the closer the PCM recording is to the smooth sine wave of the analog signal.
For the most commonly referred to as "lossless audio", it generally refers to the 16bit/44.1kHz sampling rate file format in the traditional CD format, and it is called lossless compression, because it contains 20Hz-22.05kHz. It is named after the frequency response frequency that completely covers the audible range of the human ear. Of course, various PCM format encoding high bit rate files are now very common, but as mentioned above, the high code rate does not effectively improve the PCM. The frequency response range of the sample rate is encoded, and only its sample points can be increased to obtain a smoother waveform that is more similar to analog recording.
It is also because almost all lossy compression formats are compressed and converted from the WAV format. In fact, the internal encoding is still PCM, so many MP3 devices did not support FLAC, APE, AAC, etc. because they are not Decompression of these files is supported, but never a player does not support the WAV format, because the WAV format itself is equal to the PCM stream.
WAV, APE, FLAC is the better choice?
For the current common PCM rate files, the three most common file formats are WAV, APE, and FLAC. What is the difference between these three formats?
WAV waveform files are waveform files that can be read directly by audio equipment and many software. There is basically no codec problem. Both flac and ape encode WAV, so they can exchange for smaller volume, but at the same time, when decoding is played, the resolution of the playback equipment is very sensitive (or limited by technology), and certain jitters will occur due to the analysis. The encoding is caused by the result that the playback effect is not full and smooth. This can be solved by unified conversion to WAV format.
For the WAV format, it is the largest file format in the current conventional lossless compression format. Since both FLAC and APE have higher technology coding for WAV, they are exchanged for a smaller volume, which is also the two formats. So the root cause of the emergence. For both FLAC and APE formats, although the size is similar, but different compression formats are used, so the resources that need to be occupied during playback are not the same, simply say how much resources are used. The ratio is: APE is the largest, FLAC is the smallest, and WAV is the smallest. The simplest example is that if you use a portable device that is not very expensive, such as the iPod Classic with rockbox or some of the current mainstream portable players, the use of APE will have a significant reduction in card and battery life. There is no obvious difference between FLAC and WAV.

â–²APE will stop if there is an error
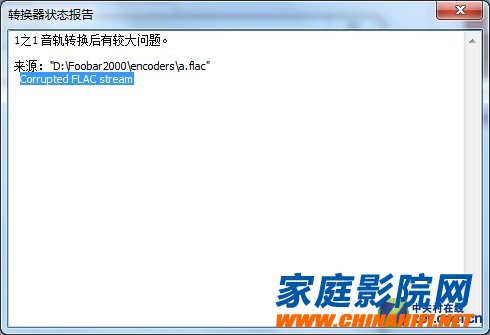
â–²FLAC format can only report errors when converting
â–²FLAC format error is muted
And in addition to the compression ratio and the occupied resources, APE, FLAC and WAV also have different errors in error correction. First of all, the most traditional WAV format does not have error correction processing, so even if there is an error in the playback rate, WAV will play as usual, and popping may occur in the wrong place. The APE stops the play directly for the error, and this is also criticized by many people. If there is an error in your APE file, the entire track is almost scrapped. FLAC uses a mute strategy. If an error occurs during playback, the error is muted.
The pros and cons of the MP3 and AAC formats for the funeral CD
For the two audio formats that currently have the most users in the world, they have two things in common: 1. They are not lossless compressed format audio. 2. They joined forces to end the CD's position in the music industry.
Perhaps for Chinese users, the MP3 format is more familiar, users are basically starting from the MP3 format until now, but AAC is indeed an audio format that cannot be ignored, it is carried forward by Apple and is monopolized in the iPod. On the road, it made a great contribution. It can even be said that AAC not only watched the CD go down the historical stage, but the traditional consumer MP3 products were also driven out of the altar. So far in the album music sales of the iTunes Store, the format of the music is still AAC instead of MP3.

â–²MP3 format is directly cut off above 20KHz
First of all, MP3 is a lossy compression format that is most familiar to domestic users. The lossy compression format that belongs to the world is innumerable. What is the reason for MP3 success? The first is its compression ratio. The traditional audio compression file only Can achieve a compression ratio of about 8:1. The MP3 format increases the compression ratio to a high ratio compression of 10:1 or even 12:1, and because the MP3 audio code has a high compression ratio of 10:1 to 12:1 while maintaining a low audio portion without distortion. But at the expense of the quality of the 12KHz to 16KHz high-audio part of the sound file in exchange for the size of the file, and completely cut off the part above 20KHz, the same length of music files, stored in .mp3 format, generally only 1 of the .wav file /10, so the sound quality is second to the sound file in CD format or WAV format. However, due to its small file size and good sound quality, no other audio formats can match it at the beginning of its development, thus providing good conditions for the development of the .mp3 format. Until now, this format is still very popular, and the status as a mainstream audio format is hard to be shaken. However, the tree has a big style, and the copyright issue of MP3 music has not been solved. Because MP3 has no copyright protection technology, it can be used by anyone.
AAC is actually an abbreviation for Advanced Audio Coding. AAC is an audio format jointly developed by Fraunhofer IIS-A, Dolby and AT&T as part of the MPEG-2 specification. The algorithm used by AAC is different from the MP3 algorithm. AAC combines other functions to improve coding efficiency. AAC's audio algorithms far surpass the previous compression algorithms (such as MP3, etc.) in compression capabilities. It also supports up to 48 tracks, 15 low frequency tracks, more sample rate and bit rate, multi-language compatibility, and higher decoding efficiency. In short, AAC can provide better sound quality than 30% smaller than MP3 files. AAC is also one of the best lossy formats available today. There are a variety of encodings, faac, and nero are common, with a bit rate of up to 448 kbps, and the difference between near-loss and lossless compression is almost impossible at a bit rate of 448 kbps.
How powerful is the popular DSD format?
In the recent HiFi circle, it can be said that a typhoon of DSD has been blown up. All the devices have started to support the DSD format overnight. Even the top players in this traditional industry have begun to rush to update their decoding devices to support the DSD format. The stream file, and for this huge size, what is the charm of SACD's unique encoding format?

â–² How powerful is DSD?
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) Direct Bitstream Digital, which is a high-resolution digital audio specification jointly announced by Sony and Philips in 1996. The new DSD technology competes with the audio technology of DVD, sampling with a 1-bit bit stream, and sampling rate. The 2.4MHz (64 times of CD 44.1kHz sampling) high sampling method directly converts the analog music signal waveform into a digital signal to store music in nearly four times the space of the CD, thus providing a better sound. The effect, because the sampling frequency is high, the sampled waveform is very round and relatively close to the original analog waveform. Moreover, since no multi-bit is used, the bit conversion program is omitted, and the distortion and noise that may be generated due to digital filtering are reduced. Also, since it is not as easy as a multi-bit system (the higher the bit is, the easier it is) is affected by power supply or external interference, so the quality is theoretically stable. The current SACD player, compatibility, whether it is a DSD supporter or a supporter of a traditional CD, will be a win-win situation. SACD (Super Audio CD) is a new generation of digital audio specifications, with ultra-high-speed sampling (2.8224MHz, 64 times the CD). The sound is continuously quantized with 0 and 1. The dynamic range of the audible frequency domain is about 120dB. The frequency domain is about 1000kHz, and the traditional analog warmth and super high resolution. The SACD multi-channel sound quality contains 6 independent audio tracks, each of which can read the complete DSD without any compression. Full DSD Bit Rate.
But in fact, the problem of DSD is very serious and obvious. Compared with the previous format problem, the problem of DSD is not in its sound quality. It can be said that the sound quality of DSD is undoubtedly excellent. But in fact, this technology has been born for nearly 20 years, and it has only been in the past two years. So where did it go for more than a decade? Some recording industry insiders have told me that Sony and Philips has priced the price of DSD recording equipment very expensive, almost no studio is willing to buy, so the DSD format will gradually die, and after a lapse of so many years, the current speaker and decoding, amplification technology can Better to show the high level of DSD, but the problem is equally obvious: did not have to listen.
Friends who really like music will find that DSD audio is basically divided into two types: PCM stream transcription and DSD direct recording. The latter rarely has an album worth listening to. Apart from some popular music, classical music has almost no good interpretation. For PCM transcription, the level of DSD is not at the source of the recording, and it becomes meaningless.
Home Theater Network () Summary:
For these types of audio formats, I believe that the readers also have a deeper understanding. For your own use needs, choosing the right music files is essential to save space and reduce your own troubles. For more home theater knowledge, welcome to follow WeChat: cnhifi.
Mouse Pad,Soft Sublimation Printed Mouse Pad,Die Cut Mouse Pad,Direct Custom Logo
Cixi Mingsheng Rubber & Plastic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.popmat.com