Part 1 of this blog series reviews the wM-Bus protocol standard in the European 868MHz ISM band. Today, let's take a closer look at the protocol version optimized for the 75 kHz narrowband in the 169.400 MHz band. This version is defined in the European Standard (EN) EN300 220 v.2.4.1 standard for monitoring, tracking, data acquisition and meter reading applications. A maximum radiated power of +500mW (or +27dBm) and a duty cycle of less than 10% enable a wide area network (WAN) approach that can cover a range of kilometers in a densely populated environment. The design approach of this approach is to combine as few, but high-precision data collector (DC) components as possible, each component capable of supporting up to 1000 endpoints (or intelligence) without the need for repeaters. meter). EN13757-4:2014-2 defines wM-Bus N mode Nabcdef and Ng by dividing the total available bandwidth of 75 kHz into six narrowband channels of 12.5 kHz. Four of the channels (Nabef) are capable of carrying a data rate of 4.8 kbps, while the other two channels (Ncd) have a data rate of 2.4 kbps and support 2-GFSK modulation. It also defines a higher data rate channel (Ng), uses 4-GFSK modulation to achieve a data rate of 19.2 kbps, and occupies a channel with a bandwidth of 50 kHz (see Figure 1).
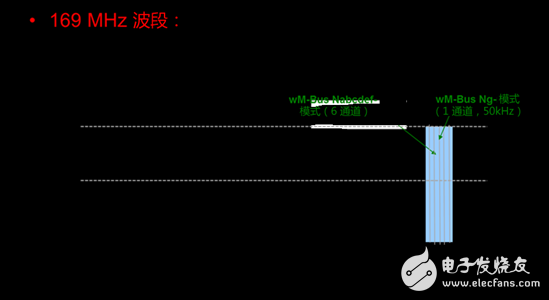
Figure 1. Relationship between wM-Bus mode N mode and ETSI 300 220 v2.4.1
This wM-Bus N mode has been adopted as an Italian and French residential gas meter, as well as an RF communication protocol for French water meters. In N mode, the highest possible receiver level (Hr) should meet the ETSI Class 2 receiver blocking requirements. In fact, because known sources of interference such as data video broadcasting (DVB) or FM radio transmitters do operate at other frequencies, their up to several kilowatts of RF power still cause some interference, even in the 169 MHz ISM band. So, for designers, it is wise to design a more challenging ETSI Class 1 specification receiver system.
So, what exactly is the ETSI Class 1 specification?
Simply put, it is the most stringent RF receiver specification for EN300 200 v2.4.1 for "high-reliability SRD communication media; for example, services for human life systems that may cause bodily harm."
One of the most challenging requirements of Class 1 specifications is proximity channel rejection/selectivity. This technical parameter measures the receiver's tolerance to interference sources that are only +-12.5 kHz away. Since this source of interference is too close to the desired signal, all cannot be filtered out with an external SAW filter. Another very challenging condition to be met is spurious response suppression, which is 60 dB at 0.1% of the RF frequency. At a frequency of 169 MHz, this value is only 169 kHz, so an RF transceiver with an IF frequency higher than 85 kHz will achieve an image frequency higher than 169 kHz and must have a rejection of more than 60 dB.
TI's high-performance Sub-1 GHz CC1120 RF transceiver family is meeting and exceeding all requirements of the N-mode wM-Bus standard (EN13757-4), including all RF requirements for Italian and French gas meter specifications. This transceiver is capable of fully receiving all N-mode messages containing a 16-bit header (including the 4-GFSK submode), and due to its WaveMatch feature, no packet loss occurs. Very fast automatic gain control is stable with only 4 data bits; if used with RX Sniff mode, it maintains maximum CC1120 sensitivity and is reduced as shown in TIDC-WMBUS-169MHz while searching for the header The average current. By using an optimized set of CC1120 register settings called "Best Blocking", an ETSI Class 1 receiver system can be implemented without the need to add expensive external surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters or LNA components. performance. The CC1120 RF Receiver is the industry's first integrated transceiver that enables ETSI Type 1 compatibility without the need for an external SAW filter and is a market leader in RF performance and robustness. You can find more technical information about the CC1120 in the TI Designs reference design TIDC-WMBUS-169MHz and TIDC-MULTIBAND-WMBUS. The CC1120 can be adjusted to "best sensitivity" or "best block" with just a few register changes. This feature enables a flexible wM-Bus N mode solution that automatically adapts to changing RF interference in the field.
In addition to the RF subsystem itself, TI has introduced innovative battery management solutions such as Energy Buffer (PMP9753) for long battery life applications, which eliminates the need for expensive mixed layer capacitor (HLC) components and can Use a variety of battery types from different vendors.
Combine battery management, N-mode compatible RF systems with a complete CIG-compatible wM-Bus stack (this stack is used in Italy and is used in advanced ultra-low power metrology devices (see for Rotation Sensing or Ultrasonic TIDM) -ULTRASONIC-FLOW-TDC's EVM430-FR6989)), TI is providing multiple optimization platforms to implement smart flowmeters that support 169MHz RF communications.
The next blog in this series talks about how to implement the next-generation single-chip wM-Bus solution for 868 and 433MHz applications with new ultra-low-power wireless microcontrollers; don't go away, keep an eye on the upcoming On the Posts on the Grid.
2.3 After fermentation Orange (Orange made enzyme solution navel orange), seized after the hand, breaking and other processes made of navel orange sauce.
Effects: lung, spleen shun gas, without any food additives, preservatives, is the first choice of children and senior citizens.
Companies registered capital of 35 million yuan, the end of 2014 the total assets of 48.69 million yuan, including fixed assets of 37.52 million yuan. The company's existing cooperation Orange cultivation base 7043.5 acres, the company production base is located in Jiangxi County Tech Industrial Park Chu Tan industrial area, covers an area of 120 acres, it has built a standard plant 9,000 square meters, Nissan 6000 kg Orange enzymes and other liquid enzyme products. Enzyme, known as enzyme, refers to a polymer substance having biocatalytic functionality. In the catalytic reaction system an enzyme, the reactant molecules are known as substrates, enzyme substrates by catalytic conversion to another molecule. Almost all cellular activity of enzymes involved in the process are required to improve efficiency. Similar to other non-biological catalysts, enzymes chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy to accelerate the rate of the reaction, most of the enzyme catalyzed reaction rate can be increased a million times; in fact, the enzyme is to provide an activation energy needs than another low way, so that more particles to have less than the activation energy of the reaction kinetic energy, thus speeding up the reaction rate. Enzyme as a catalyst, in itself is not consumed during the reaction, it does not affect the chemical equilibrium reactions. Positive enzyme catalysis, but also a negative catalytic effect, not only to accelerate the reaction rate, but also to reduce the reaction rate. And other non-living catalysts is different, having a high degree of specificity of enzyme, only a catalytic reaction or produce a particular specific configuration.
Enzyme Cream,Whitening Slimming Enzyme Cream ,Meal Replacement Diet Enzyme Cream ,Conditioning After Surgery Enzyme Cream
Ganzhou Green days Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cn-gangdao.com