2SA2151 and 2SC6100 are high-power pairs for new audio amplifiers. Based on the technical parameters provided by the manufacturer and some of their own experience in making power amplifiers, the author of this article has built a power amplifier that is very suitable for home use for several months. Now the circuit is provided as follows for your reference.
Circuit selection
The author's listening room area is 21 square meters, and the speakers are self-made imitation Ls3 / 5a two-way monitor speakers. Due to the opportunity to get in touch with various audio equipment, it was decided to make a power amplifier with a variety of sounds after comparison. The voltage amplifying part is selected in the form of operational amplifier, transistor discrete form, and tube type, and is switched by a switch for comparison. The final current amplification stage adopts 0dB pure class A without negative feedback. The circuit is shown in Figure 1. 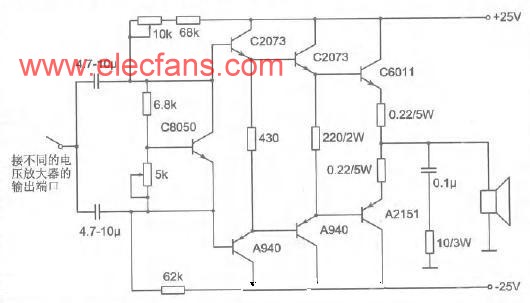
The selection of this circuit form is mainly based on the following considerations:
1. The use of pure class A working form can basically eliminate the crossover distortion and switching distortion, these two distortions can not be overcome by ordinary class B amplifiers.
2. Adopt the negative feedback form without large loop to eliminate the transient intermodulation distortion and interface intermodulation distortion caused by the loop negative feedback. Both of these distortions are dynamic indicators. Quantitative measurement of these two distortion methods is very troublesome, so there is no technical indicator for these two distortions in the whole product. Transient intermodulation distortion has a great effect on the quality of the playback sound, and generally do not pay much attention to this index. Interface intermodulation distortion is a new dynamic distortion generated by the back electromotive force generated by the voice coil when the speaker is working and acting on the amplifier input stage through the loop negative feedback. Serious intermodulation distortion at the interface will make the replayed sound turbid. All power amplifiers with large loop negative feedback have this problem, but to varying degrees.
The 3.0dB pure class A non-negative feedback power amplifier has no voltage gain, which is a test for the performance of the voltage amplification stage. Since it does not enter the negative feedback loop, other indicators such as harmonic distortion and damping factors depend on the circuit itself and the quality of the components.
Component installation and commissioning
The general current amplification stage is composed of two stages, one stage of medium power tube amplifies the current, and one stage is the high power tube for high current output. In order to adapt to the output current of different voltage amplification stages, the circuit of Fig. 1 adopts the Darlington structure in the current amplification stage so that very small current can meet the needs of the output rated power.
The pure class A output power of the circuit in Figure 1 is 25W (8Ω load), and the quiescent current is 1.25A, so that the static tube consumption of each power tube is 31.25W, and the total static power consumption of the four power tubes is 125w.
The circuit can be assembled with a printed circuit board when it is made, or it can be directly assembled on the heat sink in the form of lap welding. The area of ​​the radiator should meet the requirements during assembly. Generally, a radiator similar to the nominal 200W finished machine should be selected. When assembling with a printed circuit board, the constant voltage bias adjustment tube 8050 should be tightly attached to the heat sink for temperature compensation. The two medium power tubes of each arm should be closely attached back to back to ensure thermal equilibrium. Installed on the radiator, the power supply is directly connected to the C pole of the high-power tube. The adjustable resistance should be multi-turn precision adjustable resistance to ensure the accuracy and safety of the adjustment.
The input capacitor has a great influence on the sound, and you can choose the brand according to your own preferences. All transistors should be used in pairs. After assembling, it can be commissioned by power. First adjust the 10K adjustable resistor to make the output DC voltage below 10mV. If the DC voltage cannot be adjusted below 10mV, it means that the matching of the transistors is not good, and the readjustment should be replaced, and then adjust the quiescent current after adjustment. Adjust the 5K adjustable resistor so that the DC voltage across the emitter resistance (0.22Ω / 5W) of the high-power tube is 275mV. At this time, the static current is 1.25A. Let the amplifier stand in this state for 1 hour and then measure the midpoint DC The voltage and quiescent current values ​​are readjusted if they do not match. After the adjustment is completed, even after the production is completed, select different voltage amplification stages to work.
Selection and assembly of voltage amplification stage
Figure 2 shows the transistor voltage amplification stage. This circuit uses the pre-amplifier circuit of the famous "Marantz" PM power amplifier. When the final power amplifier needs to reach a rated output of 25W, the voltage amplifier stage should provide an undistorted voltage above 15V. The original circuit is used as a pre-amplifier. The voltage amplification factor is only 8.5 times, which cannot meet the needs. The voltage amplification factor was changed to 22 times to meet the needs of the final stage. After assembling according to the picture, adjust the 470Ω adjustable resistance to make the quiescent current of D669 and B649 to 20 mA, making it work in Class A state. 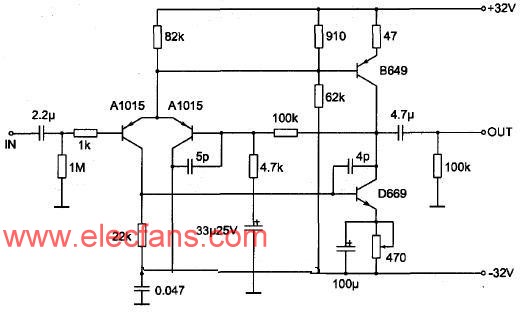
Figure 3 is a voltage amplifier stage composed of dual op amps. The choice of this circuit is mainly to appreciate the sound and sound quality of different grades of op amps. Since the maximum output voltage of the op amp is only 13V, this circuit is used to promote the maximum power at the final stage There is only 20W, and the gold-plated sockets are used in the position of the op amp during assembly to facilitate the replacement of different op amps to test the sound. 
Figure 4 shows the tube voltage amplification stage. The circuit refers to the world-famous machine "Mattis" circuit. In order to meet the needs of the final stage, some changes have been made in the power supply voltage and amplification factor. The sound of this circuit is quite sweet, and it is a good match with the pure class A final combination. The circuit is easy to assemble, no need to debug and install immediately. 
The above three voltage amplification stages should use high-quality components as far as possible during assembly, especially the coupling capacitors at all levels should choose fever-level brand capacitors.
The final working voltage of this machine is comprehensively considered under the state that the high power tube works at 1.25A. Do not easily increase the working voltage of the final power tube in order to increase the output power. If the speaker impedance is 4Ω, the pure class A power It will be reduced to 12.5W, and the power of Class A and B will increase to about 60W. Since the final power amplifier tube does not enter the loop negative feedback network, the distortion will increase significantly when the operating point enters the Class B state, so the final power should be readjusted The quiescent current and working voltage of the tube should be adjusted to 1.77A at 25W pure Class A power output at a load of 4Ω, and the working voltage should be ± 17V; at this time, the static power consumption of a single power tube is about 30W. This power can fully meet the needs in the state of home playback. It is more than enough to push a 10-inch three-way floor-standing speaker. This is the difference between pure Class A and Class B amplifiers. Interested readers can try it.
Bedroom Lights, Ceiling Light, Ceiling Light Replacement, Led Ceiling Lights
Shenzhen Dianjiang Engineering Co. LTD , https://www.isourceled.com