Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC (Electro MagneTic Compabilities) refers to the ability of a device or system to operate in its electromagnetic environment without any unacceptable electromagnetic interference to any device in its environment. Therefore, EMC includes two aspects: on the one hand, it means that the electromagnetic interference generated by the equipment in the normal operation of the equipment cannot exceed a certain limit; on the other hand, it means that the equipment has certain electromagnetic interference in the environment. Degree of immunity, ie, electromagnetic susceptibility.
First, EMC protection circuitisolation
Because the signal circuit cannot withstand voltages of the order of kilovolts, this interference must be eliminated before the input circuit, which can be converted into a current signal and then converted into heat. Earth loop current can enter the interface and flow through the entire circuit, generally requiring galvanic isolation. Isolation is an effective method in industrial systems where the connection length is long or the loop current is large.
An EDA pulse with a peak value of 30A produces tens of volts of resistance drop across the ground, but its steep rise time (30A/ns) can generate up to several hundred volts of induced voltage on the same line, enough to cause The generation of erroneous data, such a high frequency will produce skin effect, so that the line resistance increases significantly. In order to counteract this effect, a large area grounding is needed to obtain low-resistance characteristics.
A fast rising pulse will generate FTB and ESD disturbances that are capacitively coupled into the low noise region. In solving this problem, it is often erroneously to add additional windings to the main power transformer to provide an isolated power supply. This method can only lead to further diffusion of interference and affect the entire circuit.
Gas discharge tube
A butterfly capacitor filled with helium. When the voltage exceeds 100V, a plasma zone can be used to limit the maximum voltage. It can withstand higher currents with smaller leakage current. The gas discharge tube can absorb high-voltage transient pulses.
Varistors
A protection device made of a metal oxide (mainly zinc). Its function is similar to a zener diode, and its response speed is faster than that of a gas discharge tube, but its leakage current is relatively high, especially when the signal is close to the clamping voltage.
Transzorb diode
Used to limit the fast transients of low voltage signals, their power dissipation capacity is limited by their size. Similar to varistors, there is a large leakage current near the breakdown voltage.
ESD structure
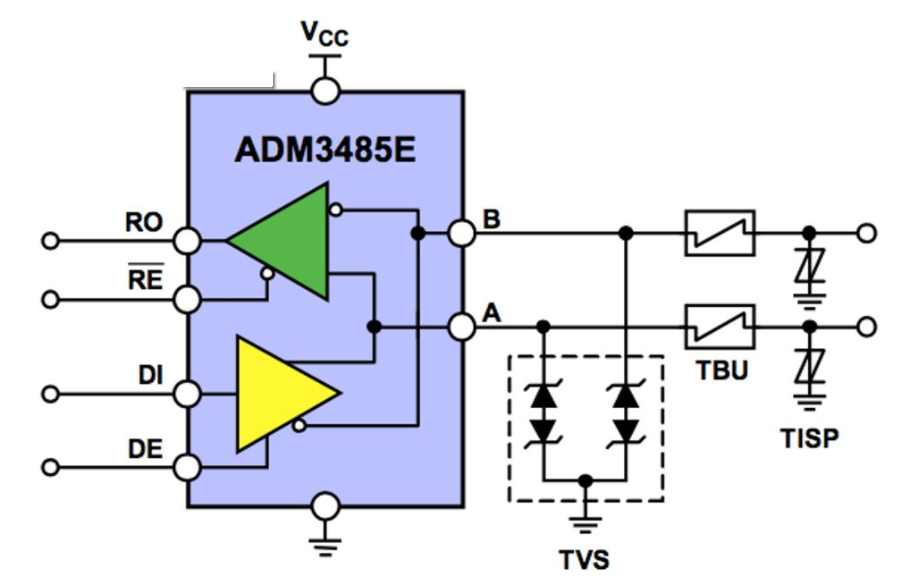
A novel design scheme that integrates bidirectional diodes in the MAX202E, MAX485E and other RS-232/rs-485/'target='_blank'>RS-485 transceiver chips. They have low capacitance and low leakage characteristics and are suitable for ESD and FTB protection.
Choke coil, ferrite
Can attenuate high frequency and fast change voltage peaks, but cannot absorb extra energy. To avoid resonance, it is always used together with a capacitor attenuator (similar to a T-type LC filter). These devices are often used to suppress common-mode interference and act as main filter components.
Capacitor
It is one of the important protection components. The parameters to be considered in the application include: Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), magnetic induction coefficient, rated current and rated voltage.
Series resistance
It is one of the important and inexpensive protection devices. The value of resistance and power dissipation value are properly selected and can replace many expensive protection devices.
Second, the application of EMC protection circuitThermocouple
To avoid signal distortion due to ground loop current effects, galvanic isolation is provided between signal acquisition and signal processing in most thermocouple applications. As shown in Figure 2, the differential signal is fed through the multiplexer to the input of the instrumentation amplifier, and then sent to the A/D converter (ADC) for conversion to a digital signal. The digital output signal of the ADC is transmitted through an optical or magnetic coupler.
The thermocouples are protected by a simple low-pass RC network (2kΩ & 100nF) per electrode. In addition, a 1nF capacitor with high voltage rating is required between the circuit common and the equipment cabinet ground. This capacitor will ESD interference bypasses ground and maintains DC current isolation. It also forms a capacitive voltage divider that reduces the peak voltage of the isolated power supply. Leakage currents generated by multiplexers, buffer amplifiers, etc. need to be considered because the leakage current will cause static signal errors when flowing through the protection series resistor.
The MAX4052A multiplexer is pin-compatible with the industry-standard 4052 device. It provides a maximum leakage current of 5nA over an extended temperature range. Typical leakage current is 2pA at 25°C, and the maximum possible error is only 2μV. This error is acceptable for most thermocouples. If an instrumentation amplifier is used for signal buffering (using the MAX4524 quad op amp), the leakage current will be reduced to 100pA in the extended temperature range, typically 1pA at 25°C. In addition, the extremely low input offset voltage drift coefficient (only 0.3μV/°C) makes this buffer ideal for high impedance, low amplitude signal sources.
Angle encoder
The angle encoder can be used to determine the position of the rotor of the motor. The precision positioning system uses dual-channel, orthogonal differential sinusoidal signals as position pointers for high-precision rotors. Such systems often require the use of an RS-485/422 serial bus to set the code. Initialization parameters, sometimes these transmission lines need to transmit analog signals of a few kHz over long distances or digital signals at a rate of several Mbit/s (see Figure 3). In this case, large resistance series resistors or passive RC networks cannot be used as protection circuits. In the figure, a termination resistor (usually 120 ohm) is used to prevent signal reflection. In order to meet the asymmetry of the transmitter and receiver common-mode voltage specifications (EIA-422A: -7V to +12V), asymmetrical protection networks are required. The entire protection network can also be replaced with the MAX490E RS-422 transceiver, which integrates ESD and FTB protection circuitry. When there is a large exchange current between two discrete grounds, a 100 Ω resistor can be placed in series between the shield and the ground, preferably with a bypass capacitor with a low ESR.
If the system requires surge protection, an external protection network is used. A desirable method is to connect a current limiting resistor in series with the line terminal. This is easy to achieve on the receiving end, it will only produce a slight signal drop. At the transmitting end, it is necessary to confirm that about 10Ω series resistance is acceptable, because the MAX490E differential output impedance is about 40Ω. In a practical circuit, a PTC fuse is generally connected in series on the data line.
Standard signal interface
A ±10V interface is often used to set the target position in motor control applications. The application environment is very noisy. Once the wiring fails, the 24V industrial power supply will be damaged. The signal line protectors MAX4506 and MAX4507 have an on-resistance of 60Ω and a maximum leakage current of 20nA over the full temperature range, providing an excellent interface protection. When a large amplitude signal passes through the chip, the system passes unaffectedly. The IC. If interference causes the protection terminal signal to exceed the supply voltage (positive or negative), the line protector will present a high impedance to this fault signal. It can withstand 36V fault voltage (±40V at power off)
Stylus Pen Tip,Stylus Pencil Tip,Carbon Fiber Pen Tip,Carbon Fiber Stylus Pen Tip
Shenzhen Ruidian Technology CO., Ltd , https://www.szwisonen.com