Xilinx's Zynq®-7000 series is based on Xilinx's fully programmed system-on-chip (SoC) architecture, integrating a feature-rich dual-core or single-core ARM® CortexTM-A9 processing system (PS) and 28nm Xilinx programmable logic. ® CortexTM-A9 CPU is the heart of the processing system, including on-chip memory, external memory interface and various peripheral connection interfaces. Mainly used in car-assisted driving, driving information and entertainment systems, broadcast cameras, industrial motor control, industrial networks And machine vision, IP and smart cameras, LTE wireless and baseband, medical diagnostics and imaging, multifunction printers, and video and night vision devices. This article describes the main features and architecture of the Zynq-7000 FPGA, as well as the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA The main features and advantages of the SoC training board, the main component map and circuit diagram.
The Zynq®-7000 family is based on the Xilinx All Programmable SoC architecture. These products integrate a feature-rich dual-core or single-core ARM® CortexTM-A9 based processing system (PS) and 28 nm Xilinx programmable logic (PL) The ARM Cortex-A9 CPUs are the heart of the PS and also include on-chip memory, external memory interfaces, and a rich set of peripheral connecTIvity interfaces.
The Zynq-7000 family offers the flexibility and scalability of an FPGA, while providing performance, power, and ease of usetypically associated with ASIC and ASSPs. The range of devices in the Zynq-7000 family allows designers to targetcost-sensiTIve as well as high -performance applicaTIons from a single platform using industry-standard tools. While eachdevice in the Zynq-7000 family contains the same PS, the PL and I/O resources vary between the devices. As a result, theZynq-7000 and Zynq-7000S SoCs Are able to serve a wide range of applicaTIons including:
• Automotive driver assistance, driver information, and infotainment
• Broadcast camera
• Industrial motor control, industrial networking, and machine vision
• IP and Smart camera
• LTE radio and baseband
• Medical diagnostics and imaging
• Multifunction printers
• Video and night vision equipment
The Zynq-7000 architecture enables implementation of custom logic in the PL and custom software in the PS. It allows for the realization of unique and differentiated system functions. The integration of the PS with the PL allows levels of performance that two-chip solutions (eg, An ASSP with an FPGA) cannot match due to their limited I/O bandwidth, latency, and power budgets.
Xilinx offers a large number of soft IP for the Zynq-7000 family. Stand-alone and Linux device drivers are available for the peripherals in the PS and the PL. The Vivado® Design Suite development environment enables a rapid product development for software, hardware, and Systems engineers. Adoption of the ARM-based PS also brings a broad range ofthird-party tools and IP providers in combination with Xilinx's existing PL ecosystem.
The inclusion of an application processor enables high-level operating system support, eg, Linux. Other standard operating systemss used with the Cortex-A9 processor are also available for the Zynq-7000 family.
The PS and the PL are on separate power domains, enabling the user of these devices to power down the PL for powermanagement if required. The processors in the PS always boot first, allowing a software centric approach for PLconfiguration. PL configuration is managed by software Running on the CPU, so it boots similar to an ASSP.
Key features of Zynq-7000 FPGA:
Processing System (PS)
ARM Cortex-A9 Based
Application Processor Unit (APU)
• 2.5 DMIPS/MHz per CPU
• CPU frequency: Up to 1 GHz
• Coherent multiprocessor support
• ARMv7-A architecture
• TrustZone® security
• Thumb®-2 instruction set
• Jazelle® RCT execution Environment Architecture
• NEONTM media-processing engine
• Single and double precision Vector Floating Point Unit (VFPU)
• CoreSightTM and Program Trace Macrocell (PTM)
• Timer and Interrupts
• Three watchdog timers
• One global timer
• Two triple-timer counters
Caches
• 32 KB Level 1 4-way set-associative instruction and data caches (independent for each CPU)
• 512 KB 8-way set-associative Level 2 cache(shared between the CPUs)
• Byte-parity support
On-Chip Memory
• On-chip boot ROM
• 256 KB on-chip RAM (OCM)
• Byte-parity support
External Memory Interfaces
• Multiprotocol dynamic memory controller
• 16-bit or 32-bit interfaces to DDR3, DDR3L, DDR2, or LPDDR2memories
• ECC support in 16-bit mode
• 1GB of address space using single rank of 8-, 16-, or 32-bit-widememories
• Static memory interfaces
• 8-bit SRAM data bus with up to 64 MB support
• Parallel NOR flash support
• ONFI1.0 NAND flash support (1-bit ECC)
• 1-bit SPI, 2-bit SPI, 4-bit SPI (quad-SPI), or two quad-SPI (8-bit) serial NOR flash
8-Channel DMA Controller
• Memory-to-memory, memory-to-peripheral, peripheral-to-memory, and scatter-gather transaction support
I/O Peripherals and Interfaces
• Two 10/100/1000 tri-speed Ethernet MAC peripherals with IEEE Std 802.3 and IEEE Std 1588 revision 2.0 support
• Scatter-gather DMA capability
• Recognition of 1588 rev. 2 PTP frames
• GMII, RGMII, and SGMII interfaces
• Two USB 2.0 OTG peripherals, each supporting up to 12 Endpoints
• USB 2.0 compliant device IP core
• Supports on-the-go, high-speed, full-speed, and low-speedmodes
• Intel EHCI compliant USB host
• 8-bit ULPI external PHY interface
• Two full CAN 2.0B compliant CAN bus interfaces
• CAN 2.0-A and CAN 2.0-B and ISO 118981-1 standardcompliant
• External PHY interface
• Two SD/SDIO 2.0/MMC3.31 compliant controllers
• Two full-duplex SPI ports with three peripheral chip selects
• Two high-speed UARTs (up to 1 Mb/s)
• Two master and slave I2C interfaces
• GPIO with four 32-bit banks, of which up to 54 bits can be used with the PS I/O (one bank of 32b and one bank of 22b) and up to 64 bits (up to two banks of 32b) connected to the Programmable Logic
• Up to 54 flexible multiplexed I/O (MIO) for peripheral pin assignments
Interconnect
• High-bandwidth connectivity within PS and between PS and PL
• ARM AMBA® AXI based
• QoS support on critical masters for latency and bandwidth control
Programmable Logic (PL)
Configurable Logic Blocks (CLB)
• Look-up tables (LUT)
• Flip-flops
• Cascadeable adders
36 Kb Block RAM
• True Dual-Port
• Up to 72 bits wide
• Configurable as dual 18 Kb block RAM
DSP Blocks
• 18 x 25 signed multiply
• 48-bit adder/accumulator
• 25-bit pre-adder
Programmable I/O Blocks
• Supports LVCMOS, LVDS, and SSTL
• 1.2V to 3.3VI/O
• Programmable I/O delay and SerDes
JTAG Boundary-Scan
• IEEE Std 1149.1 Compatible Test Interface
PCI Express® Block
• Supports Root complex and End Point configurations
• Supports up to Gen2 speeds
• Supports up to 8 lanes
Serial Transceivers
• Up to 16 receivers and transmitters
• Supports up to 12.5 Gb/s data rates
Two 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converters
• On-chip voltage and temperature sensing
• Up to 17 external differential input channels
• One million samples per second maximum conversion rate
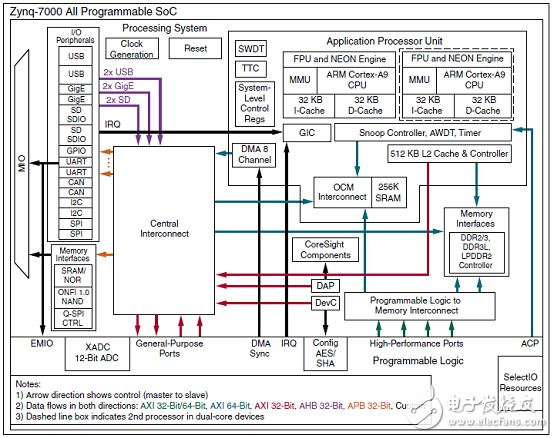
Figure 1. Zynq-7000 FPGA architecture diagram
Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board
The Zybo (ZynqTM Board) is a feature-rich, ready-to-use, entry-level embedded software and digital circuit development platform built around the smallest member of the Xilinx Zynq-7000 family, the Z-7010. The Z- 7010 is based on the Xilinx® All Programmable System-on-Chip (AP SoC) architecture, which tightly integrates a dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 processor with Xilinx 7-series field programmable gate array (FPGA) logic. When coupled with the Rich set of multimedia and connectivity peripherals available on the Zybo, the Zynq Z-7010 can host a whole system design. The on-board memories, video and audio I/O, dual-role USB, Ethernet and SD slot will have your design Up-and-ready with no additional hardware needed. Additionally, six Pmod connectors are available to put any design on an easy growth path. The Zybo provides an ultra-low cost alternative to the ZedBoard for designers that don't require the high- Density I/O of the FMC connector, but still wish to leverage the massive processing p Ower and extensibility of the Zynq AP SoC architecture.
Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Key Features and Benefits:
128 Mb Serial Flash w/ QSPI interface
16-bits per pixel VGA output port
240 KB Block RAM
28,000 logic cells
512 MB x32 DDR3 w/ 1050Mbps bandwidth
650 MHz dual-core CortexTM-A9 processor
80 DSP slices
Audio codec with headphone out, microphone and line in jacks
DDR3 memory controller with 8 DMA channels
Dual-role (Source/Sink) HDMI port
External EEPROM (programmed with 48-bit globally unique EUI-48/64TM compatible identifier)
GPIO: 6 pushbuttons, 4 slide switches, 5 LEDs
High-bandwith peripheral controllers: 1G Ethernet, USB 2.0, SDIO
Low-bandwidth peripheral controller: SPI, UART, I2C
OTG USB 2.0 PHY (supports host and device)
On-board JTAG programming and UART to USB converter
On-chip dual channel, 12-bit, 1 MSPS analog-to-digital converter (XADC)
Six Pmod ports (1 processor-dedicated, 1 dual analog/digital)
Trimode (1Gbit/100Mbit/10Mbit) Ethernet PHY
Xilinx Zynq-7000 (XC7Z010-1CLG400C)
microSD slot (supports Linux file system)
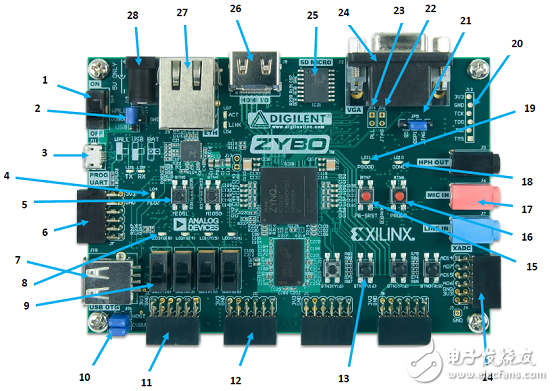
Figure 2. Outline drawing of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board
Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board number of characters correspondence table:
Figure 3. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (1)
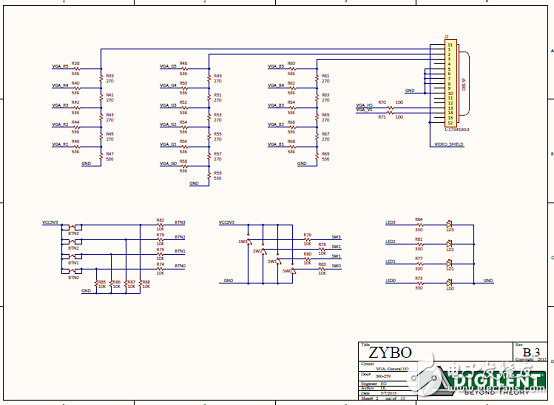
Figure 4. Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Circuit Diagram (2)
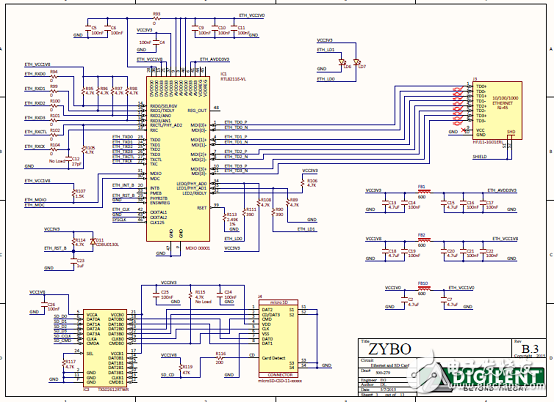
Figure 5. Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Circuit Diagram (3)
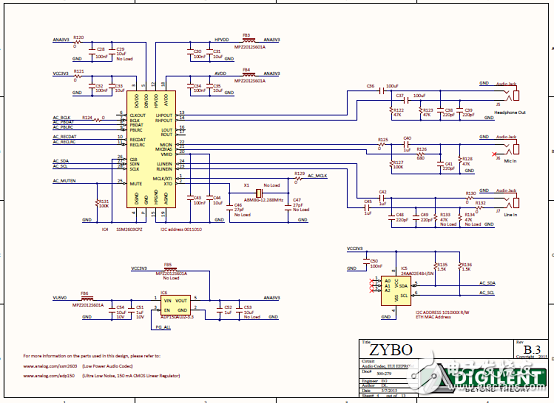
Figure 6. Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Circuit Diagram (4)
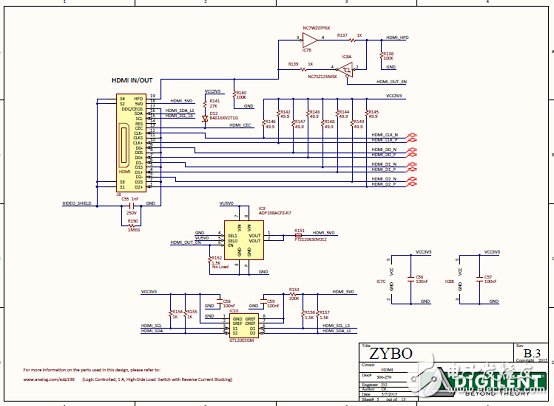
Figure 7. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (5)
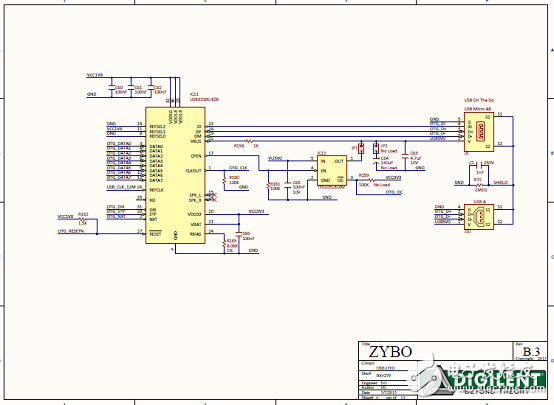
Figure 8. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (6)
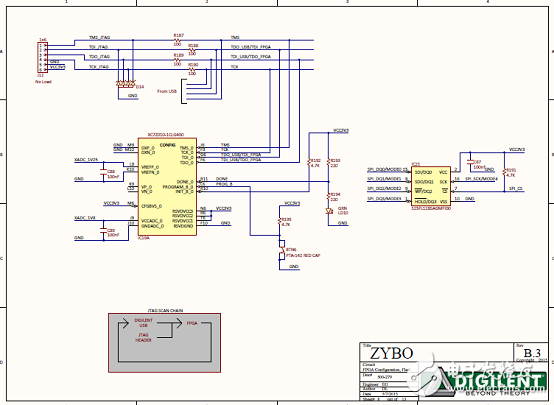
Figure 9. Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Circuit Diagram (7)
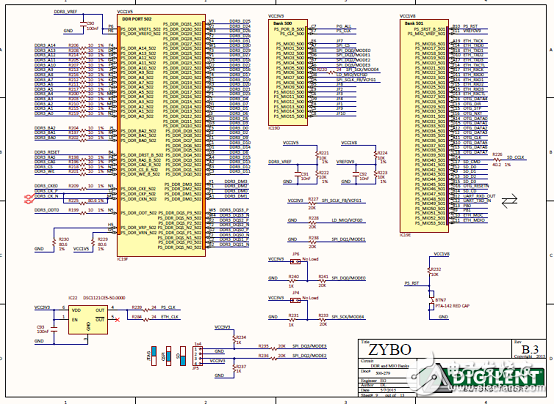
Figure 10. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (8)
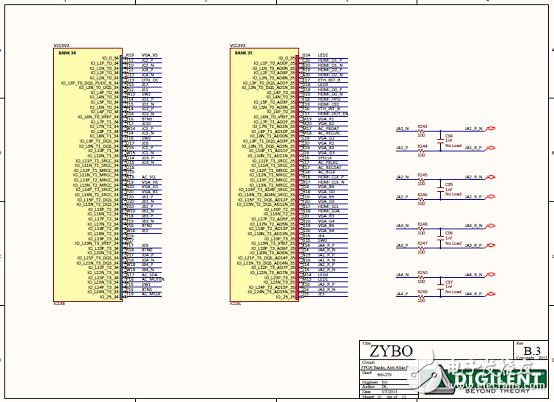
Figure 11. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (9)
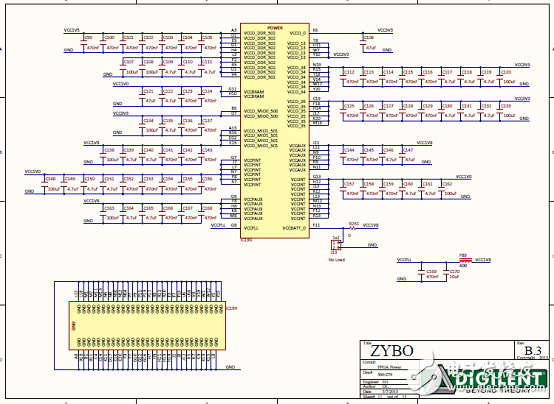
Figure 12. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (10)
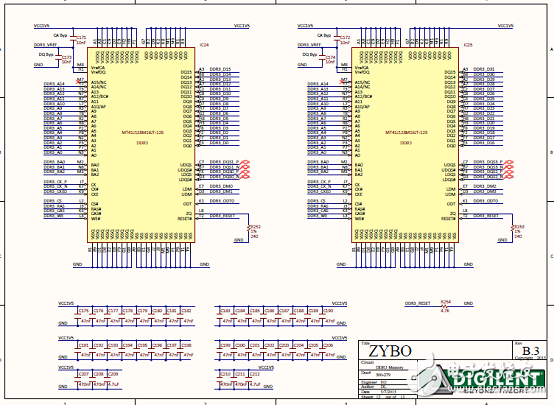
Figure 13. Circuit diagram of the Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC training board (11)
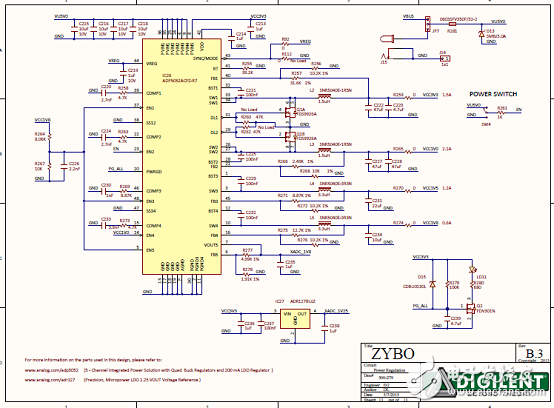
Figure 14. Zybo Zynq-7000 ARM/FPGA SoC Training Board Circuit Diagram (12)
Incremental Encoder is commonly used, and Absolute Encoder is used if there are strict requirements on position and zero position. Servo system should be analyzed in detail, depending on the application situation. Commonly used incremental encoder for speed measurement, which can be used for infinite accumulation measurement; Absolute encoder is used for position measurement, and the position is unique (single or multiple turns). Finally, it depends on the application situation and the purpose and requirements to be realized.
Incremental Linear Encoders,Linear Optical Encoder,Linear Position Encoder,Encoder Bearing Tester
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yuhengcoder.com