With the rise of smart devices, the number of people downloading content is unprecedented, which puts a lot of pressure on the network. Global wireless carriers are therefore facing increasing demands for high-speed mobile broadband services. More and more users are tempted to use bandwidth-hungry applications, such as video applications, and operators have to find new technologies to stay ahead of these growing demands.
Just as operators are trying their best to unload data traffic, 4G technology is starting to shine...
First, what is 4G?
What is 4G? If you use a simple sentence to introduce it: This is actually relative to 3G, the most popular is the fourth generation of mobile communication technology, which can provide high-speed mobile network broadband services. High speed is indeed the biggest feature of 4G. Taking the LTE standard as an example, its theoretical download speed is about 100 MB/sec, which is about 2000 times that of dial-up Internet access. At this rate, download a 600MB file in just 6 seconds. However, in practical applications, all bandwidth is affected by the transmission distance and the number of simultaneous online users. At present, ITU's basic technical requirement for 4G is to achieve a rate of 100 Mbit/s in the mobile state and a rate of 1 Gbit/s in the static and slow moving states. Compared with the existing mobile communication technology, the transmission speed of 4G can be increased by 1000 times. As the saying goes, get the standard, and get the world! Therefore, after the emergence of 4G technology, the standard dispute has become the focus of major technology vendors.
Second, the WIMAX standard of depression
The previous mainstream mobile communication standards were proposed by the communications community, mainly telecom operators, like some telecom equipment vendors, Huawei, ZTE, Ericsson, which we are familiar with. However, computer manufacturers in the 3G era due to data communication, computer manufacturers in the 3G era also began to try to put forward some of their own mobile communication technology standards, WIMAX is created in this case, the main support of WIMAX in this regard It is Intel, which is a traditional manufacturer of computer chips, and because it is developed from wireless LAN, high-rate transmission rate is its biggest feature.

WiMAX is a wireless broadband technology defined by the IEEE 802.16 standard. The earliest IEEE 802.16 standard was released in December 2001. Since then, several revisions and new versions have been released. However, the last version that really makes WiMAX a world-leading technology is IEEE 802.16-2005 (802.16e). ). Based on IEEE802.16e, 802.16-2005 can provide switching and roaming, enabling WiMAX to provide mobile applications, and is therefore considered by the industry to be an accelerator for the development of personal mobile broadband. Three key technologies, SOFDMA, MIMO and AAS, enable WiMAX to achieve further improvements in key features such as speed, throughput and capacity. These key features enable operators to provide services that require bandwidth and QoS requirements to end users, such as Streaming media, VoIP, video conferencing and interactive games.
At the beginning, the development of WiMAX was not bad, and it also occupied a place in the market. However, the future of the technology has been debated since its launch. Its weakness is proposed by computer manufacturers, so there is no ready-made example in network deployment, and the network layout of operators is a very complicated matter. Like LTE network, it evolved smoothly from the original 3G network, so it The assumption of the network is that there is considerable experience and there are quite a few mature examples. The complexity of the carrier network requires a number of ready-made examples to be continuously developed and improved. So with the WIMAX main support vendor Intel disbanding the WIMAX office in 2010, WIMAX has basically lost the opportunity to become a mainstream international standard. In this way, LTE has become the only mainstream standard in the 4G era.
Third, the LTE standard
LTE is the abbreviation of "Long Term EvoluTIon" in English. In fact, it is not difficult to understand from the English name. LTE is quite different from the current mainstream 3G technology. It can be understood that the International Telecommunication Union is a kind of exploration and attempt for future mobile communication systems. . Since it is an attempt, there must be a corresponding template. The earliest proposed LTE evolution strategy is 3GPP, which defines LTE as derived from GSM/UMTS wireless communication technology. Because we often say that CDMA2000, WCDMA, LTE, etc. are all air interfaces, the evolution path of LTE should be GSM-WCDMA-HSD/UPA-LTE.

According to the working mode, LTE can be further divided into FDD-LTE, which is a natural evolution of WCDMA. In addition, China's TDSCDM evolves into TD-LTE. The two standards fall into one LTE standard. The main difference between the two is that TD-LTE is time division multiplexing, and FDD-LTE is frequency division multiplexing. For example, TD-LTE is like an early single-track railway. Trains in two directions share a section of railroad tracks. At the same time, only one direction of trains will pass. In TD-LTE, the mobile base station and the terminal are similar. The base station transmits data to the terminal in a certain period of time, and the terminal transmits data to the base station in another time period, and the same frequency band is used for transmitting and receiving. The FDD-LTE is different. The transmission and reception uses different frequency bands, which can be carried out at the same time. Similar to the double-track railway we see now, the two-way trains take the rails and do not affect each other.
This seems to be a better FDD method, which is used in both GSM and WCDMA. But in the LTE era, TDD does have two advantages. First, FDD needs to allocate two-way frequency bands for uplink and downlink services, and a certain interval between two frequency bands is needed to avoid interference. Now due to 2G, 3G has occupied some frequency bands, and it is much more difficult to allocate bidirectional frequency bands for LTE. TD-LTE does not have this limitation, and it is entirely possible to use some frequency bands to allocate the remaining "edges". Another advantage is that in the era of voice services, the uplink and downlink voice traffic is symmetric, and the FDD mode allocates the same bandwidth for uplink and downlink. However, the development of mobile Internet will change this traffic model, and the downstream traffic will be more than the upstream traffic. The time division multiplexing method can adapt to this change by assigning different durations to the uplink and downlink, and FDD can't. Therefore, TD-LTE is widely optimistic in the international industrial chain in the era of mobile Internet where the frequency band is scarce. The reason why these two standards fall into one LTE standard is because the two technologies have a high degree of commonality, and the common technology achieves more than 90%, which makes it extremely easy to achieve compatibility, and seamless interoperability between the two.
Extended reading: the development of mobile communication technology
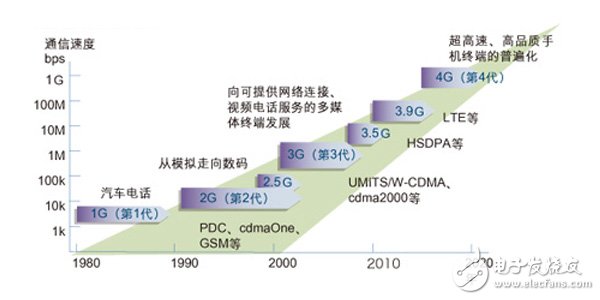
From the 1G to 4G development process, mobile communication has undergone the strengthening and upgrading of GPRS, EDGE, HSDPA and other data services. In the process, it has to undergo many improvements and evolutions, and its market application prospects are not immediate. from. It is believed that with the launch of 4G technology, the application of mobile internet will gradually mature and enrich.
Fourth, 4G has entered our world
Maybe you still think that the 4G era is far away from us! Then you are wrong. China's 3G technology started late, but in 4G, it has almost the same enthusiasm and progress as foreign countries, especially China Mobile's TD-LTE is the most active. As early as last year, China Mobile began to conduct commercial trials of 4G in Hangzhou, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen and other cities. China Mobile said that according to the actual measurement in Guangzhou and Shenzhen, the current maximum download speed of TD-LTE exceeds 80Mbps, which is about 10 times that of 3G network. For example, CCTV has a 4G network for the transmission network used in the live broadcast of the Spring Festival. China Mobile said it hopes to build 350,000 to 400,000 TD-LTE base stations nationwide in 2013.
Of course, the decision to 4G commercial is the improvement and maturity of the industrial chain, one of which is the maturity of 4G terminals. At present, all LTE chip manufacturers have or will support TD-LTE and FDD LTE common baseband chips, but the market positioning of different manufacturers is different, and the chip implementation architecture for standard protocols is different, so the process of implementing LTE multi-mode fusion and The progress is different. Currently, the main challenge for baseband chip vendors to support multimode is support for the TD-SCDMA mode. Compared with the TD-SCDMA chip industry support, the TD-LTE chip industry chain has grown stronger, including traditional TD-SCDMA chip manufacturers, traditional FDD LTE chip manufacturers, traditional WiMAX vendors and domestic emerging chip manufacturers, but with TD -SCDMA R&D vendors have a limited share of the entire TD-LTE chip industry chain. In addition, for this fast-paced 4G era, mobile phone equipment manufacturers have long been accurate. At this year's MWC2013, China Mobile's booth demonstrated several TD-LTE handsets, including Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, ZTE and Huawei, while the TD Alliance booth demonstrated Huawei, Sharp, HTC and Meiman Electronics. Waiting for more than ten companies to provide TD-LTE mobile phones. More exciting, China Mobile has launched three TD-LTE handsets in February this year. TD-LTE will have more than 1 million terminal purchases this year.
However, from the perspective of the advancement of the 4G standard, we still need to wait patiently for the full enjoyment of the 4G network----the 4G license of China has not been officially issued yet. During the delegation's residency discussions during the two sessions, the Minister of Industry and Information Technology, Miao Wei, revealed that 4G licenses are expected to be issued this year. This is the first time that the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has officially announced the issuance of 4G licenses. As for which type of license can the operator obtain? There are no clear conclusions yet. China Mobile has begun to do scale trials of TD-LTE, and obtaining TD-LTE licenses is almost a nail. China Unicom's 3G license is a WCDMA license, which can be smoothly evolved to FDD-LTE. Obtaining an FDD-LTE license is the best arrangement. The only uncertainty is China Telecom. It is worth mentioning that in the new spectrum planning scheme announced in China, 190MHz frequency resources have been given to TD-LTE in the 2.6GHz frequency band, which means that the spectrum of TD-LTE in the future is as high as 190MHz, so many spectrum resources. Obviously, a non-China Mobile operator can enjoy it. Therefore, China Telecom is likely to obtain a TD-LTE license. However, it is undeniable that the decision-making layer originally selected mobile in the development of 4G, a more important consideration is: use 4G startup to further optimize the competitive landscape of the telecommunications market. In this sense, 4G startup should not be just a matter for the three major operators, but it involves many factors such as the radio and television sector and private capital entering the telecommunications industry. And 2013 will be a key year for 4G license decisions.
Written at the end:
The vast majority of people on this planet haven't figured out what 3G is all about, and 4G is here. I wonder if you are ready for the new 4G version of the "pocket internet" era?
Notonthehighstree Notonthehighstree
Bossgoo(China)Tecgnology.(Bossgoo(China)Tecgnology) , https://www.cn-gangdao.com