The so-called threshold denoising is simply to decompose the signal, then perform threshold processing on the decomposed coefficients, and finally reconstruct the denoised signal. The main theoretical basis of the algorithm is that the wavelet transform has strong de-data correlation, which can make the energy of the signal concentrate in some small wavelet coefficients in the wavelet domain; while the energy of the noise is distributed in the whole wavelet domain. Therefore, after wavelet decomposition, the amplitude of the wavelet coefficient of the signal is greater than the amplitude of the coefficient of the noise. It can be considered that the wavelet coefficients with larger amplitudes are generally dominated by signals, while the smaller amplitude coefficients are largely noise. Thus, thresholding can be used to preserve the signal coefficients while reducing most of the noise figure to zero. The specific processing of denoising by wavelet threshold shrinkage method is: wavelet decomposition of the noisy signal on each scale, setting a threshold, the wavelet coefficient whose amplitude is lower than the threshold is set to 0, and the wavelet coefficient is higher than the threshold or Completely reserved, or do the corresponding "shrinkage" processing. Finally, the wavelet coefficients obtained after processing are reconstructed by inverse wavelet transform to obtain the denoised signal.
2. Selection of threshold functionIn the wavelet decomposition threshold denoising, the threshold function reflects different processing strategies for wavelet coefficients exceeding and below the threshold, which is a key step in threshold denoising. Let w denote the wavelet coefficient, T is the given threshold, and sign(*) is the sign function. Common threshold functions are:
Hard threshold function: (the absolute value of the wavelet coefficient is lower than the threshold, and the retention is higher than the retention)
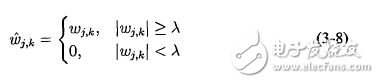
Soft threshold function: (the absolute value of the wavelet coefficient is lower than the threshold, and the higher the coefficient shrinkage processing)
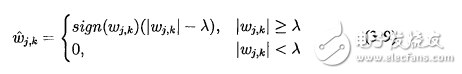
The expressions of equations (3-8) and (3-9) are:
It is worth noting that:
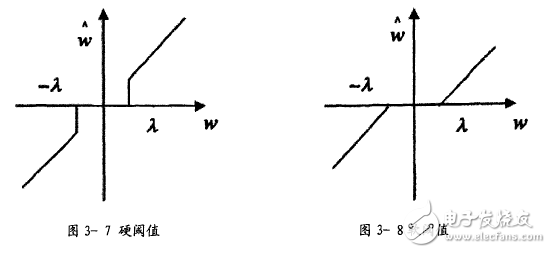
1) The hard threshold function is discontinuous at the threshold point and has been marked with black lines in the figure below. Discontinuities can cause ringing, pseudo-Gibbs effects, and so on.
2) The soft threshold function, the original coefficient and the wavelet coefficient obtained by the decomposition always have a constant deviation, which will affect the accuracy of the reconstruction.
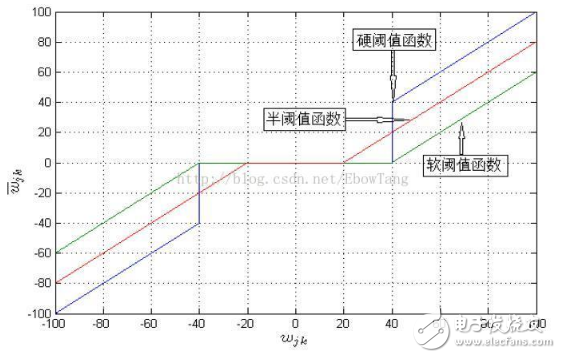
At the same time, these two functions can not express the energy distribution of the decomposed coefficients. The semi-threshold function is a simple and classic improvement scheme. See below:
The selected threshold is preferably just above the maximum level of noise. It can be proved that the maximum noise is below a very high probability (this threshold is proposed by Donoho), where the parameter to the right of the root number (called sigma) is estimated. The standard deviation of noise (according to the wavelet detail coefficient decomposed by the first stage, that is, the value of the middle position of the whole det1 absolute value coefficient), this threshold value will be used to process the detail coefficients on each scale. Note that the global threshold is the approximate coefficient. In addition to any threshold processing, the other is threshold processing.
4. Threshold strategy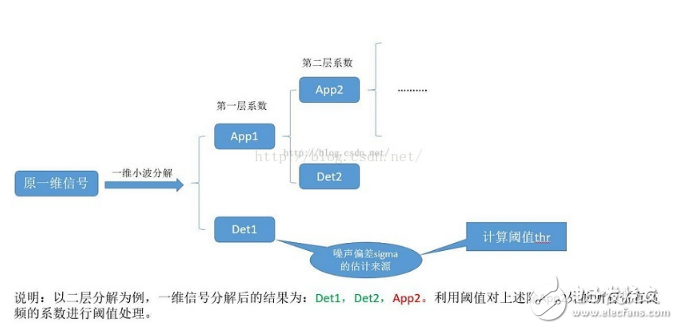
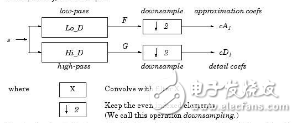
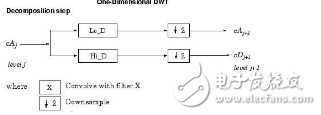
The following algorithm is described in simple text, but the signal is symmetrically extended (the default mode of matlab), and then convolved with the low-pass decomposition filter and the high-pass decomposition filter respectively, and finally downsampled. Finally, the final result can be seen. The length of the convolution sample is floor(n-1)/2+n. If you want to continue the decomposition, continue to decompose the low-frequency coefficient CA in the same way.
The lithium Battery Protection Board is the charge and discharge protection for the series-connected lithium battery pack; when fully charged, it can ensure that the voltage difference between the individual cells is less than the set value (generally ±20mV), so as to realize the equal charge of each single cell of the battery pack. , effectively improving the charging effect in the series charging mode; at the same time, it detects the overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, short circuit, and overtemperature status of each single cell in the battery pack to protect and prolong the battery life; undervoltage protection makes each A single-cell battery is used to avoid damage to the battery due to overdischarge.
Lithium Iron Battery,Lithium Iron Battery Board,Industrial Control Board,Medical PCBA Board,Circuit Board Assembly
Huizhou Liandajin Electronic Co., Ltd , https://www.ldjpcb.com