The pH value (ie, hydrogen ion concentration index, potential of hydrogen) is a measure of the pH of a water body. It is also called a hydrogen ion concentration index and a pH value. It is a scale of hydrogen ion activity in a solution, that is, a solution in the usual sense. A measure of the degree of acidity and alkalinity. pH has a wide range of uses in medicine, chemistry, and agriculture. The pH refers to the ratio of the total number of hydrogen ions in the solution to the amount of the total substance. Its value is commonly known as pH. A value indicating the degree of acidity or alkalinity of the solution, that is, a negative value of the usual logarithm of the concentration of the hydrogen ion contained.
For the determination of the hydrogen ion activity index, the qualitative method can be determined by using a pH indicator and a pH test paper, and the quantitative pH measurement needs to be performed using a pH meter.

To facilitate understanding and explanation of pH, first explain the ionization of water and the ion product constant of water.
Ionization of water : Water is a very weak electrolyte that can undergo weak ionization. Its ionization equation is: 2H2O≒H3O++OH−, abbreviated as H2O≒H++OH−, which is an endothermic process. The ionization of water is affected by temperature, and the addition of acid and alkali can inhibit the ionization of water. The ionization of water is caused by the interaction between water molecules and water molecules, so it is extremely difficult to occur. It was found that only 1 × 10−7 mol of water molecules in 1 L of pure water were ionized at 25 °C. The number of H+ and OH− ionized by water molecules is always equal in all cases. At 25 ° C, [H+] = [OH−] = 1 × 10−7 mol/L in pure water.
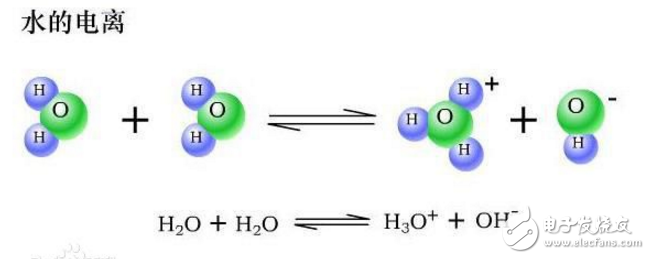
The ion product constant of water : [H+]·[OH−]=KW, where KW is called the ion product constant of water, referred to as the ion product of water; [H+] and [OH−] are the whole solution respectively. The amount of the total substance of the hydrogen ion and the hydroxide ion. KW only changes with temperature and is a temperature constant. For example, at 25 °C, [H+]=[OH−]=1×10−7mol/L, KW=1×10−14; at 100°C, [H+]=[OH−]=1×10−6mol/ L, KW = 1 × 10−12.
The basis for the acidity, neutrality or alkalinity of the solution is: the relative magnitude of the concentration of [H+] and [OH−]. The solution is acidic at any temperature [H+]"[OH−], neutral at [H+]=[OH−], and alkaline at [H+][[OH−]. However, when the [H+] and [OH−] in the solution are small, it is very inconvenient to directly use the size relationship of [H+] and [OH−] to indicate the acidity and alkalinity of the solution. In order to avoid the cumbersome calculation with the hydrogen ion concentration negative power index, the pH is mathematically defined as the common logarithm negative value of the hydrogen ion concentration, namely: pH=-lg[]. In the calculation of pH [H+] refers to the concentration of the substance of hydrogen ions in the solution, the unit is mol/L. In the dilute solution, the hydrogen ion activity is approximately equal to the concentration of hydrogen ions, and the hydrogen ion concentration can be used. Perform an approximate calculation.
pH in lifeBetween pH 1 and 2 is the toilet spirit
Between pH 2 and 3 is lemon, vinegar
pH 3 is apple
pH 3 to 4 is orange
pH 4 to 5 is soy sauce
pH 6 is watermelon, carrot
Between pH 6 and 7 is milk
Between pH 7 and 8 is egg white
Toothpaste between pH 8 and 9
pH 10 is soap
pH 11 is grass gray water
Between 12 and 13 pH is the kitchen cleaner
pH is one of the most important physical and chemical parameters of aqueous solutions. Any natural phenomenon involving aqueous solutions. Both chemical changes and production processes are related to pH, so pH needs to be measured in industrial, agricultural, medical, environmental and scientific fields.
OrpOxidation reduction potential, referred to as ORP or Eh. ORP as a comprehensive indicator of the environmental conditions of the medium (including soil, natural water, culture medium, etc.) has been used for a long time, which characterizes the relative degree of oxidative or reductive properties of the medium. The ORP measuring electrode can be made of various metals, such as nickel, copper, silver, iridium, platinum, gold, etc., which are composed of an ionic lattice structure, electrons can move inside the crystal lattice, and they also generate a potential difference due to the presence of the same kind of ions. . An ORP electrode is an electrode that can absorb or release electrons on the surface of a sensitive layer. The sensitive layer is an inert metal, usually made of platinum and gold.

The redox system used in water treatment is mainly the reduction of chromic acid and the oxidation of cyanide. If sodium disulfide or sulfur dioxide is added to the wastewater, the hexavalent chromium ion can be converted into a trivalent chromium. If chlorine or sodium hypochlorite is added, it can be used to oxidize cyanide, followed by hydrolysis of cyanogen chloride to form a cyanate salt. This chemical reaction process is called a redox reaction system. The redox potential is a measure of electron activity, which is similar to the method of measuring hydrogen ion activity.
Water disinfection and applicationThe redox electrode measures the disinfection effect on swimming pool water, mineral water and tap water. Since the bactericidal effect of coliforms in water is affected by the redox potential, the redox potential is a reliable indicator of water quality. If the redox potential value of pool water and mineral water is equal to or higher than 650 mv, it means that the bacteria content is acceptable.
Soil ORP changeObserve the dynamic changes of ORP in soil, etc.
For example, after rice paddy is planted with water, the redox status of the soil has changed drastically. There is a paddy soil viewed from the tillage layer and generally maintained at 450-650 mV before irrigation. After irrigation, the ORP drops rapidly. When the organic matter is decomposed, the ORP drops to minus 200mV to 100mV. When a large amount of fresh green manure is applied, it can even drop to minus 300mV. It will rise again in the future and is generally maintained at 0-200mV. Before the rice harvest, the soil dries and the ORP rises back above 450mV (extracted from Tianren, the physical chemistry of the paddy soil).
Other applicationsMarine exploration, bioengineering, environmental protection, brewing industry and other sectors of the national economy have been widely used.
Relationship between ph value and orpORP represents the redox potential of the solution. The ORP value is a measure of the redox capacity of an aqueous solution, and its unit is mV. The ORP meter is a special instrument for testing the redox potential of a solution. It consists of an ORP composite electrode and an mV meter. An ORP electrode is an electrode that can absorb or release electrons on the surface of a sensitive layer. The sensitive layer is an inert metal, usually made of platinum and gold. The reference electrode is the same silver/silver chloride electrode as the pH electrode.
The function of the pH electrode is to convert the hydrogen ion activity in the solution into an electromotive force, and the function of the pH meter is to measure the potential generated by the pH electrode, convert it to pH value and display it.
ORP is a brand new oxidation-reduction potential analyzer, a meter for measuring the pH of a solution.
If orp is a redox potential, then every 59.1 millivolts of potential changes by one PH unit, so PH = 7 does not say that orp is the smallest, the size is only relative, it is obvious that when PH = 1, its potential is less than PH Potential at =7
Semiconductor Moly
Semiconductor Moly
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cnpositioning.com